UNICEF seeks $27.5 million to step up cholera response in Haiti
Children account for roughly 40 per cent of the confirmed cholera cases in Haiti, or two in five, the UN Children’s Fund (UNICEF) said on Wednesday, appealing for $27.5 million to save more lives from the disease.
The outbreak began two months ago and is unfolding amid economic crisis and rising insecurity due to gang violence.
Ninety per cent of confirmed cases have been in areas with a high burden of severe acute malnutrition.
A ‘triple threat’
Children suffering from the condition, which is also known as severe wasting, are more vulnerable to cholera and at least three times more at risk of dying from it.
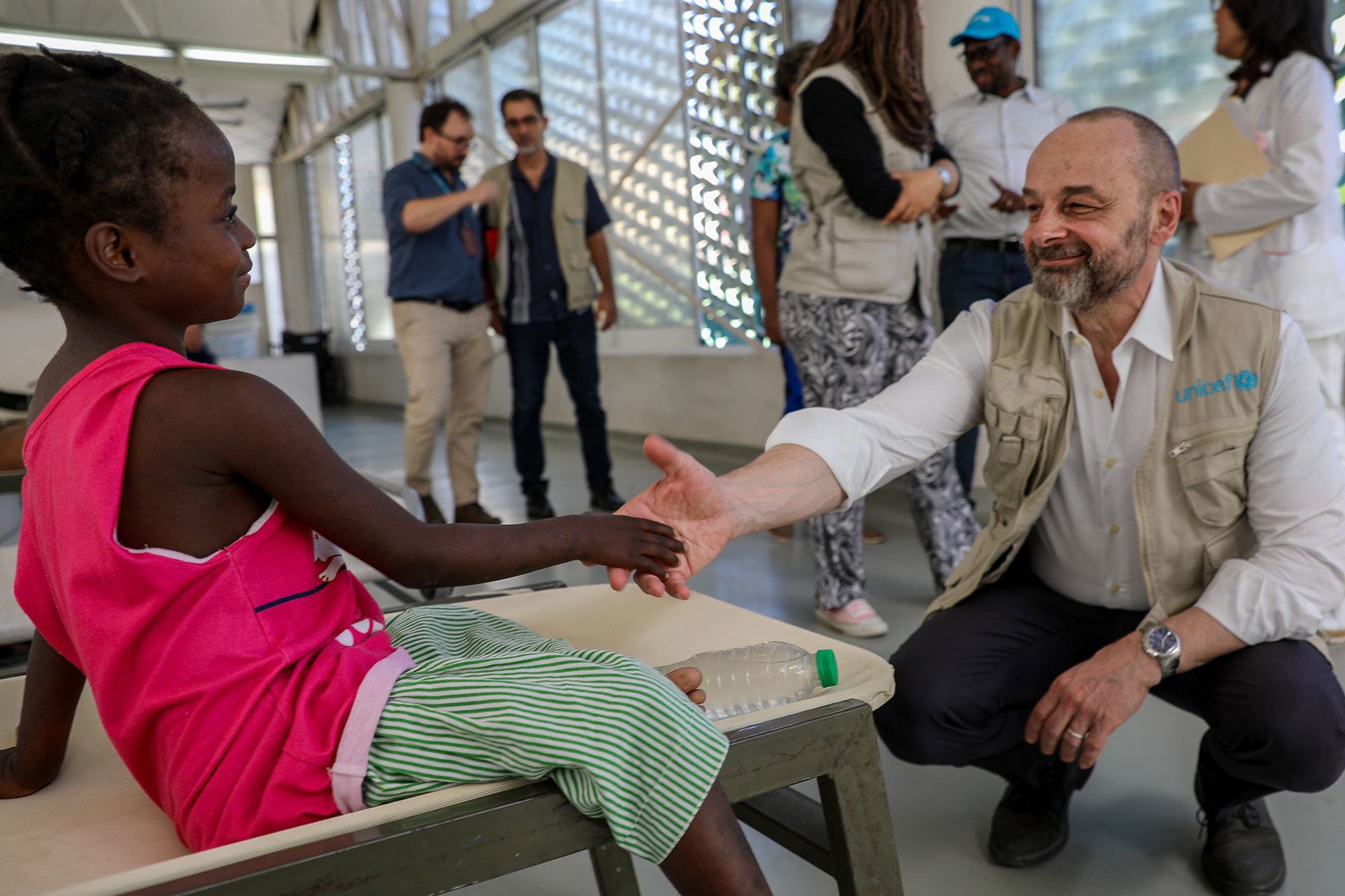
“In Haiti right now, there is a triple threat to children’s lives –malnutrition, cholera and armed violence. And sometimes all three together,” said Manuel Fontaine, Director of UNICEF’s Office of Emergency Programmes, who has concluded a four-day visit to the country.
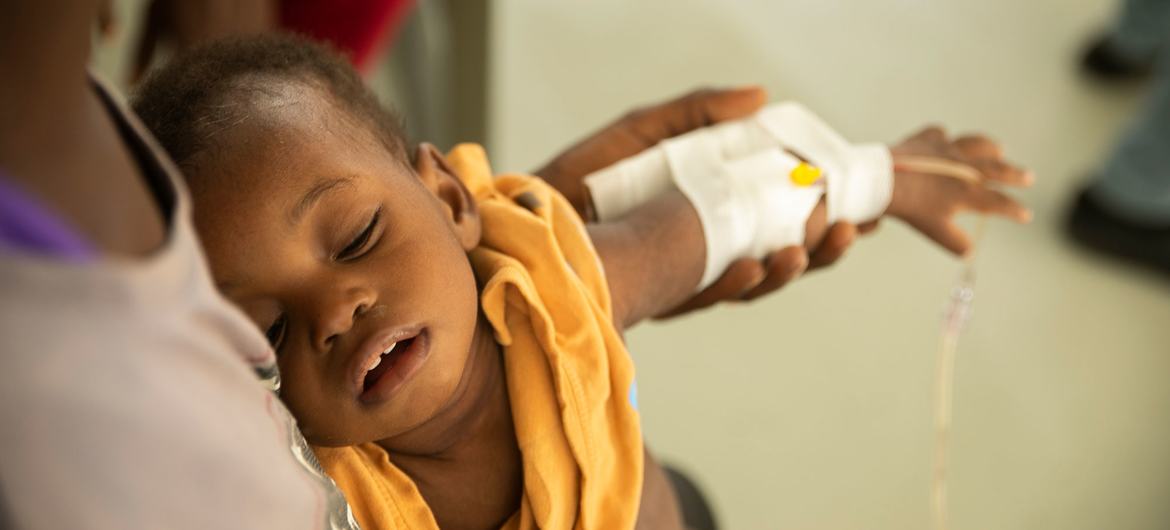
Mr. Fontaine saw how malnourished children are receiving life-saving care at UNICEF-supported cholera treatments in the capital, Port-au-Prince, and in the Cité Soleil neighbourhood there.
“I was shocked to see many children at risk of dying in the cholera treatment centres. In just a few hours, acute watery diarrhoea and vomiting dehydrate and weaken them so much they may die without timely and adequate treatment. Cholera and malnutrition are a lethal combination, one leading to the other,” he said.
The senior official also went to a centre which provides medical, psychological, and psychosocial care to survivors of gender-based violence.

Breaking a ‘vicious cycle’
As of Monday, there were 924 confirmed cholera cases in Haiti, more than 10,600 suspected cases, and 188 deaths, according to the Ministry of Health.
Mr. Fontaine was adamant that the “vicious cycle” between malnutrition and cholera can be broken.
“Simple, affordable and effective treatment can save Haitian children’s lives, as long as we reach the most vulnerable families before it’s too late,” he said.
“But the urban-poor areas most affected by the cholera outbreak are also under the control of heavily armed gangs. Amid widespread armed violence and insecurity in large parts of the capital, humanitarian teams are walking on eggshells.”
Nutritional screenings and support
UNICEF is seeking the funding to ramp up its cholera response over the next five months.
The $27.5 million will be used to provide humanitarian assistance in the areas of health, water, hygiene and sanitation, as well as nutrition and protection, for 1.4 million people
Since July, the UN agency and partners have screened and assessed the nutritional status of nearly 6,200 children in Cité Soleil, the largest urban-poor area in the capital.
Overall, around 2,500 under-fives suffering from severe and moderate acute malnutrition received quality treatment.
UNICEF, in coordination with the national authorities and partners, have delivered items to health departments, such as 245 cholera kits, 313,000 oral rehydration salts sachets, zinc, antibiotics, and personal protective equipment (PPE).
Other assistance has included providing 135,000 water purifying tablets to a partner hospital in Cité Soleil.
Additionally, more than 468,000 litres of water were distributed to 22,290 people currently living in, or displaced from, the neighbourhood.