‘Shadow’ of persistent inequality is growing, key UN human development report reveals
While health, education, and income levels have improved overall across the globe, “wide inequalities” both among and within countries, are casting a shadow on sustained human development, a new United Nations report shows.
Looking at the widening gap in real terms, a child born in Norway today – the country with the highest human development index (HDI) – can expect to live beyond the age of 82, and spend almost 18 years in school. But the same child, if born in Niger – the lowest HDI – can expect only to live to 60, with just five years of formal education.
“While these statistics present a stark picture in themselves, they also speak to the tragedy of millions of individuals whose lives are affected by inequity and lost opportunities, neither of which are inevitable,” said Achim Steiner, the Administrator of the UN Development Programme (UNDP), which released the report today.
Inequality occurs in many countries, including in some of the wealthiest ones, but it ends up taking a much bigger toll on countries with lower HDI levels; with low HDI countries losing almost a third of their human development capacity. For countries with a high HDI, the average loss is 11 per cent.
The striking differences both within and among countries, are stifling progress and the trend can be seen again and again, according to UNDP.
“Inequality in all its forms and dimensions, between and within countries, limits people’s choices and opportunities, withholding progress,” explained Selim Jahan, Director of the Human Development Report Office at UNDP.
Women’s empowerment remains a particular challenge
A key sources of inequality within countries is the gap in opportunities, achievements and empowerment between women and men. On average, the HDI for women is 6 per cent lower than that for men, notes the report.
Inequality in all its forms and dimensions, between and within countries, limits people’s choices and opportunities, withholding progress – Selim Jahan, UNDP
Furthermore, while there has been “laudable progress” in the number of girls attending school, there remain big differences in other key aspects of men and women’s lives – for instance labour force participation rates for women globally are lower than for men – 49 per cent, versus 75 per cent.
And when women are working, their unemployment rates are 24 per cent higher than their male counterparts. Women globally also do much more unpaid domestic and care work than men.
“Women’s empowerment remains a particular challenge,” underscored UNDP.
Data tells a part of the story, quality of growth matters
The Human Development Report 2018 update also shows “tremendous” variation between countries in quality of education, healthcare and many other key aspects of life.
This quality-difference can be illustrated by looking at the number of students per teacher, in primary schools. Sub-Saharan Africa has, on average, 39 pupils per teacher while in developed regions, there is an average of one teacher for every 16-18 primary school pupils.
Similar difference exists in terms of health care: OECD (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development) countries and East Asia and the Pacific have, on average, 29 and 28 physicians for every 10,000 people respectively. In South Asia overall, there are only eight per 10,000, falling to less than two, in Sub-Saharan Africa.
“Much of the world’s attention is on data that tells only a part of the story about people’s lives,” said Mr. Jahan, highlighting that it is clearly not enough simply to count how many children are in the classroom. The important dimension is to know whether they are learning anything.
“Focusing on quality is essential to foster sustainable and sustained human development progress.”
UN News spoke with Mr. Jahan about the report’s findings. Listen to the interview here.
Key Findings from the 2018 Analysis
The world has made impressive progress in human development
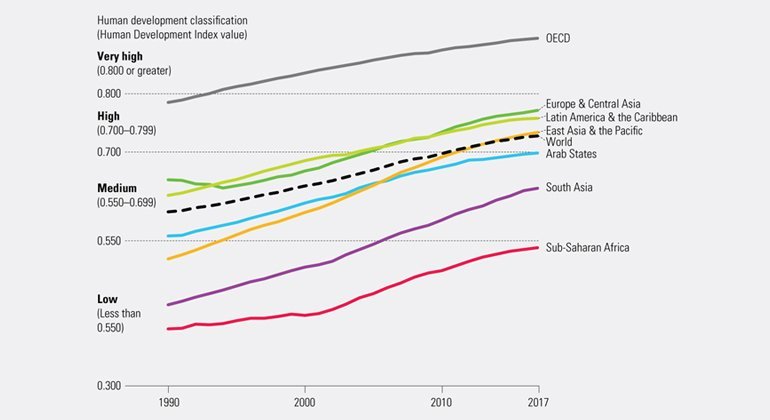
Looking back over almost three decades, all regions and human development groups have made substantial progress.
The global HDI value in 2017 was 0.728, up about 21.7 percent from 1990. Across the world, people are living longer, are more educated and have greater opportunities.
Quality, not just quantity of human development, is important, and it reveals large deficits
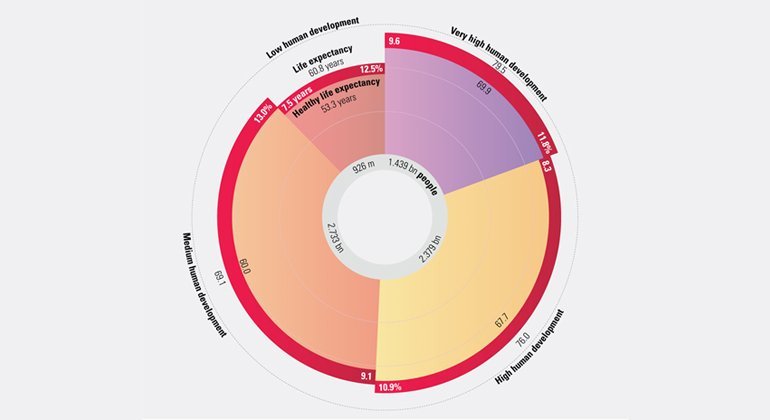
Most people today live longer, are more educated and have more access to goods and services than ever before. But living longer does not automatically mean more years spent enjoying life.
For example, healthy life expectancy for countries of very high human development is approximately 70 years, whereas for countries of low human development it is approximately 53 years.
Progress is not linear or guaranteed, and crises and challenges can reverse gains. Countries experiencing conflict show HDI losses, which can be felt for generations
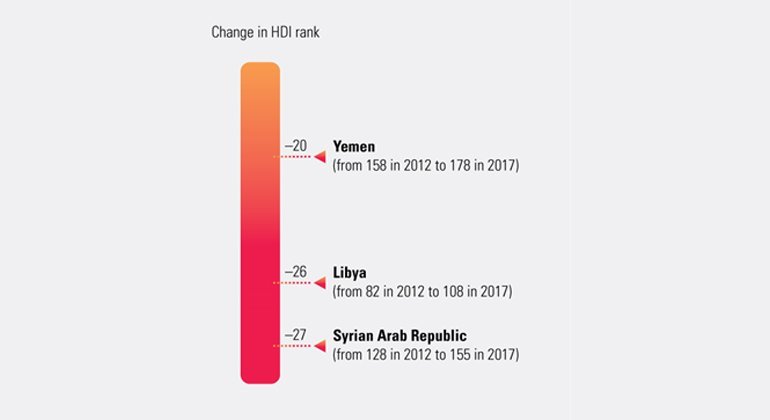
Between 2012 and 2017, Libya, Syria and Yemen had falling HDI values and ranks – the direct effect of violent conflict. Although Lebanon is not directly involved in violent conflict, it has suffered spillovers from the conflict in Syria, hosting more than a million Syrian refugees.
Disparities between and within countries continue to stifle progress
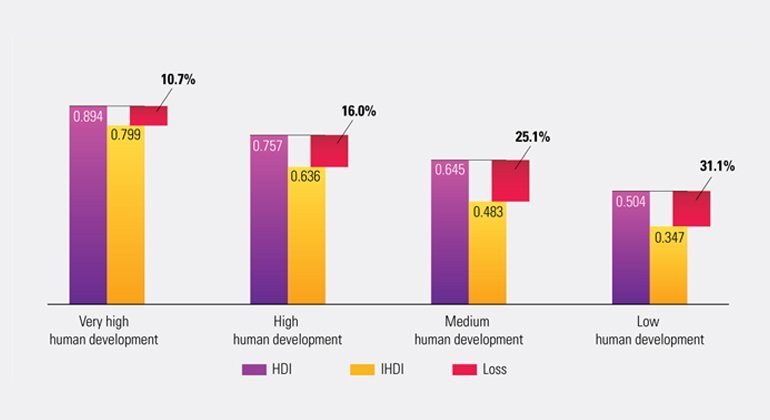
Average HDI levels have risen significantly since 1990 – 22 percent globally and 51 percent in least developed countries. But there remain massive differences across the world in people’s well-being.
Gender gaps in early years are closing, but inequalities persist in adulthood
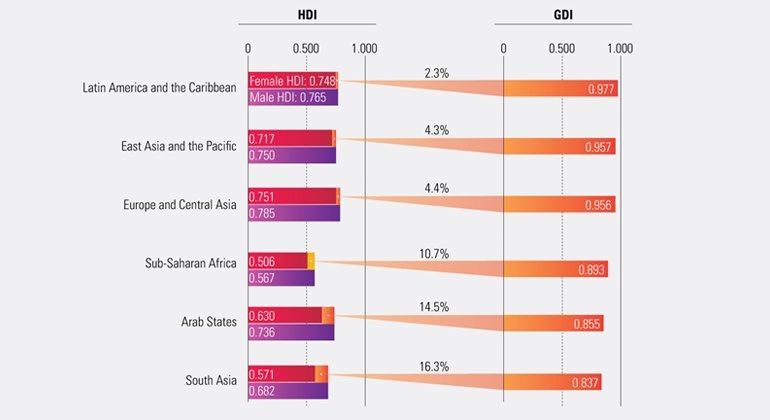
One key source of inequality within countries is the gap in opportunities, achievements and empowerment between women and men. Worldwide the average HDI for women is six percent lower than for men, due to women’s lower income and educational attainment in many countries.
Although there has been laudable progress in the number of girls attending school, there remain big differences between other key aspects of men and women’s lives. Women’s empowerment remains a particular challenge.
Global labor force participation rates for women are lower than for men – 49 percent versus 75 percent. And when women are in the labor market, their unemployment rates are 24 percent higher than their male counterparts. Women globally also do much more unpaid domestic and care work than men.
Environmental degradation puts human development gains at risk
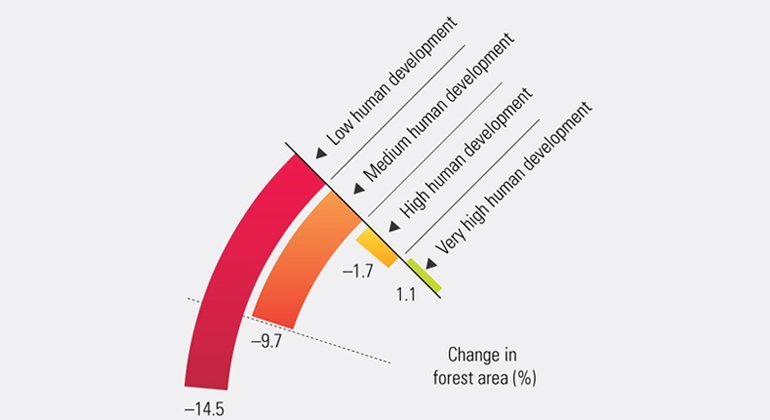
The degradation of the environment and atmosphere, coupled with significant declines in biodiversity, is linked to other development concerns ranging from declining food and water supplies to losses of livelihood and life from extreme weather events. This profoundly serious crisis threatens the human development of current and future generations.
All graphics: Human Development Report statistical update 2018, UNDP

