South Sudan: UNICEF sounds alarm on ‘catastrophic’ food insecurity in country
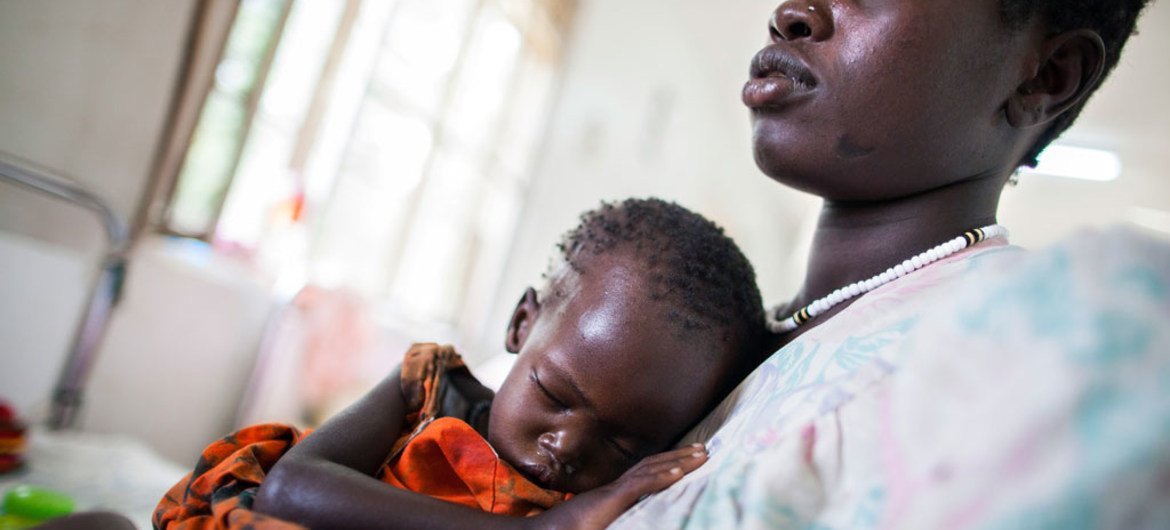
“The situation in South Sudan is catastrophic, and even more so for children,” UNICEF spokesperson Christophe Boulierac told a news briefing in Geneva, where he also pointed out that so far this year, the agency has treated 120,000 children under age five for severe malnutrition; a nearly 50 per cent increase over the same period in 2015.
Initially, UNICEF had been planning to provide support to 166,000 children in 2016, but that figure has been revised to more than 250,000, he added.
Seven out of the country’s 10 states have reached the malnutrition-rate-emergency threshold of 15 per cent, while in Northern Bahr el Ghazal, the malnutrition rate stands at 33 per cent, he explained.
UNICEF has also noted a sharp rise in malnutrition in South Sudan’s urban areas, including the capital, Juba, where the rates of children admitted for malnutrition to UNICEF-supported Al-Sabbah children’s hospitals were some 20 per cent higher in the first six months of 2016 than for the same period last year. The spokesperson cited the country’s inflation rate as one of the main reasons for the high increase, explaining that it made basic household staples too expensive for many families.
Mr. Boulierac stated that while UNICEF could not provide figures of children dying from starvation, “one quarter of a million children in South Sudan are facing severe malnutrition.”
According to the spokesperson, with a number of roads inaccessible, the ongoing conflict has further limited UNICEF’s ability to respond – leaving, in the most urgent cases, the more expensive option of air transport for delivering supplies.
Additionally, Mr. Boulierac stressed that “due to insecurity and the rainy season, UNICEF staff in South Sudan are unable to be fully mobile and deliver their goods and services.”
Mr. Boulierac said that of the $154.5 million UNICEF needs for South Sudan in 2016, the Fund had, to date, received only $52 million to assist with water and sanitation; child support services; nutrition; health; and education.
He indicated that more than 900,000 children have been displaced in the country, which – with 1.8 million children, or 51 per cent of school-age youngsters out of school – also had the highest proportion of out-of-school children in the world.
“An estimated 16,000 children had been recruited by armed groups, and there were concerns that the renewed violence would lead to a further expansion of that practice,” explained the spokesperson.
He also called attention to the fact that sexual violence and rape had been used as a weapon of war, saying “all the ingredients were there to be extremely concerned.”
Between 8 and 25 July, at least 72 civilian deaths and 217 cases of sexual violence had been documented in Juba alone.
The spokesperson for the Office of the UN High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR), William Spindler, added that the total number of South Sudanese refugees in the region stood at 917,418 – most of whom are sheltering in Uganda.
The recent fighting in South Sudan between rival forces – the Sudan People’s Liberation Army (SPLA) loyal to President Salva Kiir and the SPLA in Opposition backing First Vice-President Riek Machar – erupted in and around Juba, on 7 July, close to the fifth anniversary of its independence.
The young country has faced ongoing challenges since a political face-off between the two leaders erupted into conflict in December 2013. The crisis has produced one of the world's worst displacement situations with immense suffering for civilians.